Nitroglycerin,
regardless of the dosage form, is converted to nitric oxide (NO) once in the
body. It is commonly used in the treatment of angina (chest pain) in
patients with underlying ischemic heart disease (IHD). Since IHD can
result in decreased coronary blood perfusion to the heart, the use of
nitroglycerin can help vasodilate these vessels to increase coronary perfusion,
thereby reducing the severity of angina.
Nitric
oxide causes vasodilation through a combination of cellular processes.
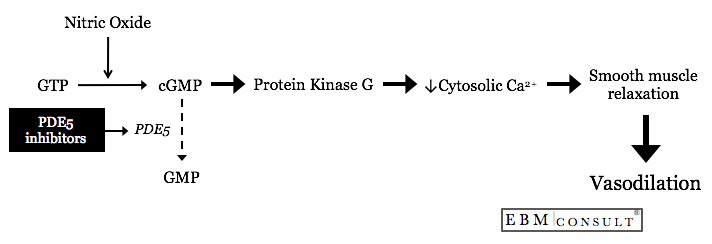
The first is by activation of guanylate cyclase, which promotes the conversion
of guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP).1,2 The
increasing cGMP binds to regulatory binding sites for protein kinase G thereby
activating the catalytic units that enable protein kinase G to reduce cytosolic
Ca2+ levels needed for smooth muscle contraction within blood vessels.1,2
In addition, NO is also known to cause direct activation of Ca2+-dependent K+ channels
resulting in a hyperpolarization and relaxation of vascular smooth muscle cells
that allow for increased blood flow.3
The problem with the co-administration of a
type-5 phosphodiesterase (PDE5) inhibitor [i.e., sildenafil (Viagra); tadalafil
(Cialis); vardenafil (Levitra)] with a nitrate has to do with their effects on
cGMP. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors are most commonly prescribed for the
treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED) and work by selectively blocking PDE5,
the enzyme necessary for the degradation of cGMP.4 The accumulation of
cGMP in the corpus cavernosum of the penis results in the increased
vasodilation necessary for an erection.4 Therefore when both nitrates and
PDE5 inhibitors are administered closely together (within the past 24 hours for
sildenafil and vardenafil and within the past 36 hours for tadalafil due to its
longer half-life), the PDE5 inhibitor prevents the breakdown of NO mediated
increases in cGMP. This results in a greater effect of cGMP to cause a
greater degree of vasodilation. This degree of vasodilation can result in
clinically significant reductions in blood pressure or hypotension.5 The
most prominent example of this interaction is when patients taking PDE5
inhibitors for their ED are given nitrates in the emergency department for
acute coronary syndrome with resultant drops in blood pressure. This
problem became significant enough that the American Heart Association published
a position statement reminding providers to consider this interaction when
using nitrates for this cardiac condition.6
References:
- Lincoln TM, Cornwell TL. Towards an understanding of the mechanism
of action of cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP in smooth muscle relaxation.
Blood Vessels 1991;28(1-3):129-37.
- Lincoln TM, Cornwell TL. Intracellular cyclic GMP receptor proteins. FASEB J 1993;7(2):328-38.
- Bolotina VM, Najibi S, Palacino JJ et al. Nitric oxide directly
activates calcium-dependent potassium channels in vascular smooth
muscle. Nature 1994;368(6474):850-853.
- Boolell M, Allen MJ, Ballard SA et al. Sildenafil: an orally
active type 5 cyclic GMP-specific phosphodiesterase inhibitor for the
treatment of penile erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res
1996;8(2):47-52.
- Webb DJ, Muirhead GJ, Wulff M et al. Sildenafil citrate
potentiates the hypotensive effects of nitric oxide donor drugs in male
patients with stable angina. J Am Coll Cardiol 2000;36(1):25-31.
- Cheitlin MD, Hutter AM Jr, Brindis RG et al. Use of sildenafil
(Viagra) in patients with cardiovascular disease. Technology and
Practice Executive Committee. Circulation 1999;99(1):168-77.