Simvastatin (Zocor): Drug Monograph
|
|---|
- Adjunct to diet to decrease total cholesterol, LDL, apolipoprotein B, and TG levels, and to increase HDL levels in primary hyperlipidemia or mixed dyslipidemia, hypertriglyceridemia, primary dysbetalipoproteinemia, homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (boys and girls who are at least 1 year postmenarche, 10-17 years of age)
- Reduce risk of coronary heart disease mortality and cardiovascular events
- Hyperlipidemia:
- 10 or 20 mg by mouth once a day in the evening
- Usual range: 5 - 40 mg by mouth once a day
- High risk for coronary heart disease events: 40 mg/day initially
- Note: Lipid determinations should be performed after 4 weeks of therapy and periodically thereafter
- Homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia:
- 40 mg by mouth once a day in the evening
- Note: Lipid determinations should be performed after 4 weeks of therapy and periodically thereafter
- Heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, 10-17 years (at least 1 year postmenarche):
- 10mg once a day in the evening
- Range: 10-40 mg/day
- Adjust at ≥4-week intervals
- Maximum: 40 mg/day
- Active liver disease, which may include unexplained persistent elevations in hepatic transaminase levels:
- Contraindicated
- Concomitant administration of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors
- Concomitant administration of gemfibrozil, cyclosporine, or danazol
- Hypersensitivity to any component of this medication
- Active liver disease, which may include unexplained persistent elevations in hepatic transaminase levels
- Women who are pregnant or may become pregnant
- Nursing mothers
- Increased risk of myopathy including rhabdomyolysis with the 80-mg dose
- Skeletal muscle effects
- Liver enzyme abnormalities - persistent elevations in hepatic transaminases can occur.
- A few cases of overdosage with ZOCOR have been reported; the maximum dose taken was 3.6 g. All patients recovered without sequelae.
- Supportive measures should be taken in the event of an overdose.
- The dialyzability of simvastatin and its metabolites in man is not known at present.
- Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors: itraconazole, ketoconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole, erythromycin, clarithromycin, telithromycin, HIV protease inhibitors, boceprevir, telaprevir, nefazodone. Gemfibrozil, cyclosporine, danazol
- Verapamil, dilitazem, dronedarone: maximum dose of 10 mg/day
- Amiodarone, amiodipine, ranolazine: maximum dose of 20 mg/day
- Lomitapide: reduce dose by 50% if initiating lomitapide
- Niacin-containing products for Chinese patients taking lipid-modifying doses (≥1 g/day): caution with doses >20 mg/day; do not give 80 mg dose
- Avoid grapefruit juice
- Pregnancy: Pregnancy category X
- Labor and Delivery: None
- Nursing Mothers: It is unknown if simvastatin is excreted in human milk. Women who are breastfeeding should not use simvastatin.
- Renal Impairment: Caution should be exercised when simvastatin is administered to patients with severe renal impairment.
- Hepatic Impairment: Simvastatin is contraindicated in patients with active liver disease, which may include unexplained persistent elevations in hepatic transminase levels.
- Pediatric Patients: Simvastatin has not been studied in patients younger than 10 years of age, nor in pre-menarchal girls. Doses greater than 40 mg have not been studied in patients 10-17 years of age. Patients 10-17 years of age treated with simvastatin had an adverse reaction profile similar to that of patients treated with placebo.
- Geriatric Patients: Prescribed with caution in the elderly.
- It is unknown if simvastatin is excreted in human milk. Women who are breastfeeding should not use simvastatin.
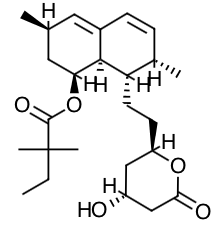
- Scientific Name: Butanoic acid, 2,2-dimethyl-,1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-[2-(tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl)-ethyl]-1-naphthalenyl ester, [1S-[1α,3α,7β,8β(2S*,4S*),-8aβ]].
- Empirical Formula: C25H38O5
- Molecular Weight: 418.57
- Simvastatin is a prodrug and is hydrolyzed to its active β-hydroxyacid form, simvastatin acid, after administration. Simvastatin is a specific inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase, the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate, an early and rate limiting step in the biosynthetic pathway for cholesterol. In addition, simvastatin reduces VLDL and TG and increases HDL-C.
- Epidemiological studies have demonstrated that elevated levels of total-C, LDL-C, as well as decreased levels of HDL-C are associated with the development of atherosclerosis and increased cardiovascular risk. Lowering LDL-C decreases this risk. However, the independent effect of raising HDL-C or lowering TG on the risk of coronary and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality has not been determined.
- Simvastatin is a lactone that is readily hydrolyzed in vivio to the corresponding β-hydroxyacid, a potent inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase. Although the mechanism is not fully understood, cyclosporine has been shown to increase the AUC of statins. The increase in AUC for simvastatin acid is presumably due, in part, to inhibition of CYP3A4. The risk of myopathy is increased by high levels of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory activity in plasma. Inhibitors of CYP3A4 can raise the plasma levels of HMB-CoA reductase inhibitory activity and increase the risk of myopathy.
- Absorption: Tmax = 1.3-2.4 hours
- Distribution: Both simvastatin and its β-hydroxyacid metabolite are highly bound (approximately 95%) to human plasma proteins.
- Metabolism: Simvastatin is not an inhibitor of CYP3A4 and therefore, is not expected to affect the plasma levels of other drugs metabolized by CYP3A4. Liver (extensive 1st pass), by hydrolysis via CYP3A4; β-hydroxyacid, 6'-hydroxy, 6'-hydroxymethyl, and 6'-exomethylene derivatives (major active metabolites)
- Elimination: Following an oral dose of 14C-labeled simvastatin in man, 13% of the dose was excreted in urine and 60% in feces. Plasma concentrations of total radioactivity (simvastatin plus 14C-metabolites) peaked at 4 hours and declined rapidly to about 10% of peak by 12 hours post dose. Since simvastatin undergoes extensive first-pass extraction in the liver, the availability of the drug to the general circulation is low (<5%).
- Adhere to their National Cholesterol Education Program recommended diet and adhere to a regular exercise program
- Have periodic testing of a fasting lipid panel
- Advise patients about substances they should not take with simvastatin. Inform other healthcare professionals prescribing a new medication or increasing the dose of an existing medication that they are taking simvastatin.
- Inform patients of the risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis and to report any unexplained muscle pain, tenderness or weakness particularly if accompanied by malaise or fever. Risk of myopathy is increased with use of the 80-mg dose. The risk of myopathy in increased when taking certain types of medication or consuming grapefruit juice. Discuss all medication, both prescription and over the counter, with their healthcare professional.
- It is recommended that liver function tests be performed before the initiation of simvastatin and when clinically needed. Promptly report any symptoms that may indicate liver injury, including fatigue, anorexia, right upper abdominal discomfort, dark urine or jaundice.
- Women of childbearing age should be advised to use an effective method of birth control to prevent pregnancy. Discuss when to stop taking simvastatin if trying to conceive. Advise patients to stop taking simvastatin if they become pregnant and call their healthcare professional.
- Women who are breastfeeding should not use simvastatin. Discuss options with their healthcare professional.
Indications
Dosing (Adult)
Dosing (Pediatric)
Hepatic Dosing
Contraindications
Warnings
Overdose
Drug Interactions
Special Populations
Breasfeeding
Chemical Structure
Mechanism of Action
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacokinetics
Counseling Points
MESH Terms & Keywords
|
|---|
|