Eluxadoline (Viberzi): Drug Monograph
|
|---|
- GI Agent (Miscellaneous)
- A mu- & kappa-opioid receptor agonist and delta-receptor antagonist
- General Dosing & Administration Notes:
- Take with food
- IBSD:
- 100 mg by mouth twice daily
-
If patient is unable to tolerate 100 mg, reduce to 75 mg twice daily
- IBSD (Patient without a gallbladder):
- 75 mg by mouth twice daily
- IBSD (with OATP1Bi inhibitors):
- 75 mg by mouth twice daily
-
Discontinue in patients who develop severe constipation for more than 4 days
- Mild or moderate (Child-Pugh Class A or B) impairment:
- 75 mg twice daily
- Severe (Child-Pugh Class C) impairment:
- Do not administer
- Known or suspected biliary duct obstruction, or sphincter of Oddi disease or dysfunction
- Patients with alcoholism, alcohol abuse, alcohol addiction, or drink more than 3 alcoholic beverages/day
- History of pancreatitis; structural diseases of the pancreas, including known or suspected pancreatic duct obstruction
- Severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C)
- Severe constipation or sequelae from constipation, or known or suspected mechanical gastrointestinal obstruction
- Sphincter of Oddi spasm and pancreatitis - monitor patients without a gallbladder for new or worsening abdominal pain, with or without nausea and vomiting, or acute biliary pain with liver or pancreatic enzyme elevations; discontinued treatment and seek medical attention if symptoms develop
- No reported overdoses
- Stomach should be emptied and adequate hydration maintained. Observe patient carefully and give standard supportive treated as needed
- Administration of a narcotic mu-opioid antagonist, such as naloxone, should be considered. Repeated administration may be necessary; monitor subject closely for the return of overdose symptoms
- OATP1B1 inhibitors - Increased exposure to eluxadoline when coadministered with cyclosporine. Administer eluxadoline at a dose of 75 mg twice daily and monitor for impaired mental or physical abilities needed to perform potentially hazardous activities
- CYP inhibitors (Strong) - potential for increased exposure to eluxadoline; monitor patients for impaired mental or physical abilities needed to perform potentially hazardous activities
- Drugs that cause constipation - increased risk for constipation related adverse reactions and potential for constipation related serious adverse reactions. Loperamide may be used occasionally for acute management of severe diarrhea but avoid chronic use. Discontinue loperamide immediately if constipation occurs
- OATP1B1 and BCRP substrate - eluxadoline may increase the exposure of such co-administered substrates. Increased risk of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis. Use the lowest effective dose of rosuvastatin
- CYP3A substrates with narrow therapeutic index - potential for increased exposure of co-administered drug. Monitor drug concentrations or other pharmacodynamic markers of drug effect when concomitant use with eluxadoline is initiated or discontinued.
- Pregnancy: Pregnancy Category not established
- Labor and Delivery: None
- Nursing Mothers: No data available regarding the presence of eluxadoline in human milk
- Renal Impairment:
- Hepatic Impairment: Plasma concentration of eluxadoline increase in patients with impairment. Contraindicated in patients with severe impairment. Administer reduce dose to patients with mild or moderate impairment. Monitor patients with any degree of impairment.
- Pediatric Patients: Safety and effectiveness have not been established.
- Geriatric Patients: No overall differences in effectiveness; a higher proportion of elderly patients experience adverse reaction, serious adverse reactions, and gastrointestinal adverse reactions compared to younger patients
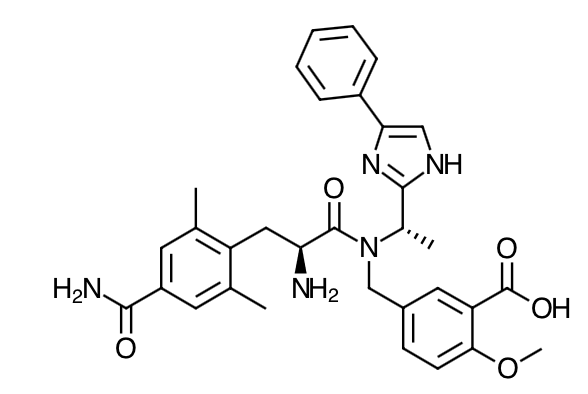
- Scientific Name: 5-[[[(2S)-2-amino-3-[4-(aminocarbonyl)-2,6-dimethylphenyl]-1 oxopropyl][(1S)-1-(4-phenyl-1H-imidazol-2-yl)ethyl]amino]methyl]-2-methoxybenzoic acid
- Empirical Formula: C32H35N5O5
- Molecular Weight: 569.65
- Eluxadoline is a mu-opioid receptor agonist; eluxadoline is also a delta opioid receptor antagonist and a kappa opioid receptor agonist. The binding affinities (Ki) of eluxadoline for the human mu and delta opioid receptors are 1.8 nM and 430 nM, respectively. The binding affinity (Ki) of eluxadoline for the human kappa opioid receptor has not been determined; however, the Ki for guinea pig cerebellum kappa opioid receptor is 55 nM. In animals, eluxadoline interacts with opioid receptors in the gut.
- Cardiac electrophysiology: At a dose 10- times the maximum recommended dose (100 mg), eluxadoline does not prolong the QT interval to any clinically relevant extent.
- Absorption: Absolute bioavailability of eluxadoline has not been determined. The median Tmax value is 1.5 hours (range: 1-8 hours) under fed conditions and 2 hours (range: 0.5-6 hours) under fasting conditions. The administration with a high fat meal that contained approximately 800 to 1000 total calories, with 50% of calories being derived from fat content decreases the Cmax of by 50% and AUC by 60%.
- Distribution: Plasma protein binding is 81%.
- Metabolism: The mean plasma elimination half-life ranges from 3.7 hours to 6 hours.
- Elimination: Following a single oral dose of 300 mg [14C] eluxadoline in healthy male subjects, 82.2% of the total radioactivity was recovered in feces within 336 hours and less than 1% was recovered in urine within 192 hours.
- Specific Populations
- Hepatic Impairment: Following a single oral 100-mg dose in subjects with varying degrees of liver impairment and healthy subjects, mean eluxadoline plasma exposure was 6-fold, 4-fold, and 16-fold higher in mild, moderate, and severe hepatically impaired subjects (Child Pugh Class A, B, C), respectively, compared to the subjects with normal liver function
- In vitro Assessment of Drug Interactions
- In vitro studies indicate that eluxadoline is neither an inducer of CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP3A4, nor an inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 at clinically relevant systemic concentrations. Although CYP2E1 was slightly inhibited by eluxadoline (IC50 of approximately 20 micromolar [11 mcg/mL]), clinically meaningful interactions are unlikely. The in vitro studies were not adequate to establish the potential for eluxadoline to inhibit CYP3A4 in the gut. In vitro studies suggest that eluxadoline is a substrate for OAT3, OATP1B1, BSEP and MRP2, but not for OCT1, OCT2, OAT1, OATP1B3, P-gp and BCRP. Based on the in vitro studies, clinically meaningful interaction via inhibition of OCT1, OCT2, OAT1, OAT3, OATP1B3, BSEP and MRP2 by eluxadoline is unlikely. However, the in vitro studies were not adequate to establish the potential for eluxadoline to inhibit P-gp in the gut.
- In Vivo Assessment of Drug Interactions
- Oral Contraceptives: Coadministration of multiple doses of 100 mg with multiple dose administration of an oral contraceptive (norethindrone 0.5 mg/ethinyl estradiol 0.035 mg) does not change the exposure of either drug.
- Cyclosporine: Coadministration of a single dose of 100 mg eluxadoline with a single dose of 600 mg cyclosporine resulted in 4.4-fold and 6.2-fold increase in AUC and Cmax of eluxadoline, respectively, compared to administration of eluxadoline alone.
- Probenecid: Coadministration of a single dose of 100 mg eluxadoline with a single dose of 500 mg probenecid resulted in a 35% and 31% increase in eluxadoline AUC and Cmax respectively, compared to administration of eluxadoline alone. This change in eluxadoline exposures is not expected to be clinically meaningful.
- Rosuvastatin: Coadministration of multiple doses of 100 mg eluxadoline twice daily with a single dose 20 mg rosuvastatin resulted in an increase in the AUC (40%) and Cmax (18%) of rosuvastatin compared to administration of rosuvastatin alone. Similar results were observed with the active, major metabolite, n-desmethyl rosuvastatin
- Instruct patients to stop treatment and seek medical attention if unusual or severe abdominal pain develops, especially if they do not have a gallbladder.
- Advise patients to avoid chronic or acute excessive alcohol use while taking eluxadoline.
- Instruct patients that if they miss a dose, take the next dose at the regular time; do not take 2 doses at the same time.
- Advise patients to call their healthcare provider if they are unable to tolerate the medication.
- Advise patients to discontinue treatment and call their healthcare provider if they experience constipation lasting more than 4 days.
- Advise patients to not take aolestron with eluxadoline or not take loperamide on a chronic basis due to the potential for constipation. Loperamide may occasionally be used with eluxadoline for acute management of severe diarrhea, but must be discontinued if constipation develops. Also, instruct patients to avoid taking eluxadoline with other medications that may cause constipation (for example opioids, anticholinergics, etc.).
Drug Class
Dosing (Adult)
Hepatic Dosing
Contraindications
Warnings
Overdose
Drug Interactions
Special Populations
Chemical Structure
Mechanism of Action
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacokinetics
Counseling Points
MESH Terms & Keywords
|
|---|
|