Drug Monograph: Rosuvastatin (Crestor)
|
|---|
- Adjunct to diet to reduce elevated total cholesterol, LDL, apolipoprotein B, and TG levels and to increase HDL levels in primary hyperlipidemia or mixed dyslipidemia, hypertriglyceridemia, primary dysbetalipoproteinemia, heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH) (adolescent boys and girls, who are at least 1 year postmenarche, 10-17 years of age)
- Treatment of homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH)
- Slow progression of atherosclerosis
- Prevention of cardiovascular disease
- Hypercholesterolemia (Hyperlipidemia and Mixed Dyslipidemia; Hypertriglyceridemia; Primary Dysbetalipoproteinemia (Type III Hyperlipoproteinemia); Slowing of the Progression of Atherosclerosis):
- 10 - 20 mg by mouth daily
- Range: 5 - 40 mg daily
- When initiating treatment or switching from another HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, use the appropriate starting dose 1st, then titrate according to patient's response and individualized goal of therapy
- Analyze lipid levels within 2-4 weeks and adjust dose accordingly
- Use 40 mg dose only if LDL goal is not achieved with 20 mg dose
- Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia (HoFH):
- 20 mg by mouth daily, then adjust dose every 2 - 4 weeks to max dose of 40 mg per day
- Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease:
- Note: Reduce the risk of stroke, MI, arterial revascularization procedures in patients without clinically evident coronary heart disease but with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease based on age (men ≥50 years of age and women ≥60 years of age), hsCRP≥2 mg/L, and the presence of at least 1 additional CVD risk factor.
- Dose: 5 - 40 mg by mouth once daily
- Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia, 10-17 years (at least 1-year postmenarche):
- 5 - 20 mg by mouth once a day
- Adjust dose at intervals of ≥4 weeks
- Max Dose: 20 mg per day
- Known hypersensitivity to product components
- Active liver disease, which may include unexplained persistent elevations in hepatic transaminase levels
- Women who are pregnant or may become pregnant
- Nursing mothers
- Skeletal muscle effects, muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness
- Liver enzyme abnormalities - persistent elevations in hepatic transaminases can occur
- Cyclosporine
- Gemfibrozil
- Lopinavir/Ritonavir or atazanavir/ritonavir
- Coumarin anticoagulants
- Concomitant lipid-lowering therapies
- Pregnancy: Pregnancy Category X
- Labor and Delivery: None
- Nursing Mothers: It is unknown if rosuvastatin is excreted in human milk. Since HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors have a potential to cause serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, women who require rosuvastatin treatment should be advised not to nurse their infants.
- Renal Impairment: Severe renal impairment (not on hemodialysis). Starting dose is 5 mg, not to exceed 10 mg
- Hepatic Impairment: Contraindicated in patients with active liver disease. Use with caution in these patients.
- Pediatric Patients: Patients treated with 5 mg, 10 mg, or 20 mg daily rosuvastatin had an adverse experience profile generally similar to that of patients treated with placebo.
- Geriatric Patients: No overall differences in safety or effectiveness. Greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
- Asian Population: Consider 5 mg starting dose.
- It is unknown if rosuvastatin is excreted in human milk. Since HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors have a potential to cause serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, women who require rosuvastatin treatment should be advised not to nurse their infants.
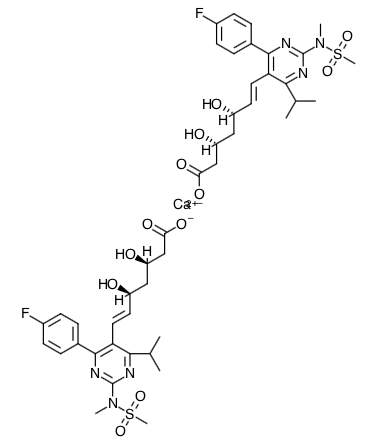
- Scientific Name: bis[(E)-7-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6isopropyl-2-[methyl(methylsulfonyl)amino]pyrimidin-5-yl](3R,5S)-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid] calcium salt
- Empirical Formula: (C22H27FN3O6S)2Ca
- Molecular Weight: 1001.14
- Rosuvastatin is a selective and competitive inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, the rate-limiting enzyme that converts 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A to mevalonate, a precursor of cholesterol. In vivo studies in animals, and in vitro studies in cultured animal and human cells have shown rosuvastatin to have a high uptake into, and selectivity for action in the liver, the target organ for cholesterol lowering. In in vivo and in vitor studies, rosuvastatin produces its lipid-modifying effects in two ways. First, it increases the number of hepatic LDL receptors on the cell-surface to enhance uptake and catabolism of LDL. Second, rosuvastatin inhibits hepatic synthesis of VLDL, which reduces the total number of VLDL and LDL particles.
- Absorption: In clinical pharmacology studies in man, peak plasma concentrations of rosuvastatin were reached 3 to 5 hours following oral dosing. Both Cmax and AUC increased in approximate proportion to rosuvastatin dose. The absolute bioavailability of rosuvastatin is approximately 20%.
- Distribution: Mean volume of distribution at steady state of rosuvastatin is approximately 134 liters. Rosuvastatin is 88% bound to plasma proteins, mostly albumin. This binding is reversible and independent of plasma concentrations.
- Metabolism: Rosuvastatin is not extensively metabolized: approximately 10% of a radiolabeled dose is recovered as metabolite. The major metabolite is N-desmethyl rosuvastatin, which is formed principally by cytochrome P450 2C9, and in vitro studies have demonstrated that N-desmethyl rosuvastatin has approximately one-sixth to one-half the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory activity of the parent compound. Overall, greater than 90% of active plasma HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory activity is accounted for by the parent compound.
- Elimination: Following oral administration, rosuvastatin and its metabolites are primarily excreted in the feces (90%). The elimination of half-life (t 1/2) of rosuvastatin is approximately 19 hours. After an intravenous dose, approximately 28% of total body clearance was via the renal route, and 72% by the hepatic route.
- Do not change the dose or stop rosuvastatin without talking to the healthy care provider who prescribed it.
- Wait at least two hours after taking rosuvastatin to take an antacid that contains a combination of aluminum and magnesium hydroxide.
- If a dose of rosuvastatin is missed, take it as soon as possible. However, do not take 2 doses within 12 hours of each other.
- Instruct patients to call their health care provider if they experience muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness especially with fever.
- Instruct patients to call their health care provider if they experience any of the following symptoms of liver problems:
- Feel unusually tired or weak
- Loss of appetite
- Upper belly pain
- Dark urine
- Yellowing of the skin or the whites of the eyes
- Inform patient of the potential hazard to fetus if the patient becomes pregnant while on therapy.
Indications
Dosing (Adult)
General Notes: Take at any time of day, with or without food. Swallow tablet whole. Do not take 2 doses within 12 hours of each other.
Dosing (Pediatric)
Contraindications
Warnings
Drug Interactions
Special Populations
Breasfeeding
Chemical Structure
Mechanism of Action
Pharmacokinetics
Counseling Points
MESH Terms & Keywords
|
|---|
|