Aripiprazole (Abilify): Drug Monograph
|
|---|
- Oral treatment for:
- Treatment of schizophrenia
- Acute treatment of manic or mixed episodes associated with bipolar I disorder as monotherapy and as an adjunct to lithium or valproate
- Maintenance treatment of bipolar I disorder, both as monotherapy and as an adjunct to lithium or valproate
- Adjunctive treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD)
- Treatment of irritability associated with autistic disorder
- As an injection for the:
- Acute treatment of agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar I disorder
- General Dosing Considerations:
- Oral formulation: administer once daily without regard to meals.
- IM injection: wait at least 2 hours between doses. Maximum daily dose 30 mg.
- The oral solution can be substituted for tablets on a mg-per-mg basis up to the 25 mg dose level. Patients receiving 30 mg tablets should receive 25 mg of the solution.
- The dosing for the orally disintegrating tablets is the same as for the oral tablets.
- Schizophrenia:
- (Adults): 10-15 mg by mouth per day up to a max of 30 mg per day.
- (Pediatrics): 2 mg by mouth per day up to a max of 30 mg per day.
- Bipolar Mania (Adults) as Monotherapy:
- (Adults): 15 mg by mouth per day up to a max of 30 mg per day
- Bipolar Mania (Adults) as Adjunct to Lithium or Valproate:
- (Adults): 10-15 mg per day up to 30 mg per day.
- (Pediatrics): 2 mg by mouth per day up to a max of 30 mg per day
- Major Depressive
Disorder (Adults) as an Adjunct to Antidepressants:
- 2-5 mg per day and increase the dose weekly by 5 mg/day (as needed) up to 15 mg per day.
- Agitation Associated with Schizophrenia or Bipolar Mania:
- 9.75 mg/1.3 mL injected IM with options to repeat the dose ≥ 2hrs up to a max 30 mg/per day.
- Irritability Associated with Autistic Disorder:
- (Pediatrics): 2 mg per day up to 15 mg per day.
- Tablets: 2 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg
- Orally disintegrating tablets: 10 mg, 15 mg
- Oral solution: 1 mg/mL (150 mL bottle)
- Injection (IM solution): 9.75 mg/1.3 mL single-dose vial
- Injection (IM suspension reconstituted): 300 mg, 400 mg (as Abilify Maintena)
- Increased mortality in elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis and suicidal thoughts and behaviors: Aripiprazole is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis.
- Children, adolescents, and young adults taking antidepressants for major depressive disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders are at increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior. Monitor appropriately and observe closely for clinical worsening suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior.
- Aripiprazole is not approved for use in pediatric patients with depression.
- Body temperature regulation - appropriate care is advised when prescribing for patients who will be experiencing conditions which may contribute to an elevation in core body temperature (e.g., exercising strenuously, exposure to extreme heat, receiving concomitant medication with anticholinergic activity, or being subject to dehydration)
- Dysphagia - use with caution in patients at risk for aspiration pneumonia
- Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis - increased incidence of cerebrovascular adverse events (e.g., stroke, transient ischemic attack, including fatalities)
- Metabolic changes - may include hyperglycemia/diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, and body weight gain
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome - manage with immediate discontinuation and close monitoring
- Orthostatic hypotension - use with caution in patients with known cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease
- Leukopenia, neutropenia, and agranulocytosis - patients with history of a clinically significant low white blood cell count (WBC) or a drug-induced leukopenia/neutropenia should have their complete blood count (CBC) monitored frequently during the first few months of therapy. Discontinuation of treatment should be considered at the first sign of a clinically significant decline in WBC in the absence of other causative factors
- Seizures/convulsions - use cautiously
- Suicidal thoughts and behaviors in adolescents and young adults - increased risk of suicidality in children, adolescents and young adults with major depressive disorder
- Suicide - closely supervise high-risk patients
- Tardive dyskinesia - discontinue if clinically appropriate
- Common adverse reactions include vomiting, somnolence, and tremor. Other clinically important signs and symptoms include:
- Acidosis, aggression, aspartate aminotransferase increased, atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, coma, confusional state, convulsion, blood creatine phosphokinase increased, depressed level of consciousness, hypertension, hypokalemia, hypotension, lethargy, loss of consciousness, QRS complex prolonged, QT prolonged, pneumonia aspiration, respiratory arrest, status epilepticus, and tachycardia.
- An electrocardiogram should be obtained and if QT interval prolongation is present, cardiac monitoring should be instituted.
- Supportive therapy, maintaining an adequate airway, oxygenation and ventilation, and management of symptoms are appropriate.
- An early charcoal administration may be useful in partially preventing the absorption of aripiprazole.
- Hemodialysis is unlikely to be useful in overdose management since aripiprazole is highly bound to plasma proteins.
- CYP450 Enzyme (Substrate): CYP2D6 and CYP3A4
- Inhibitors of CYP3A4: (e.g., ketoconazole) or CYP2D6 (e.g., fluoxetine) - will increase aripiprazole drug concentrations. Reduce aripiprazole dose to one-half of the usual dose when used concomitantly except when used ad adjunctive treatment with antidepressants. If a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor and strong CYP2D6 inhibitor are coadministered or a known CYP2D6 poor metabolizer is receiving a concomitant strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, the aripiprazole dose should be reduced to one-quarter (25%) of the usual dose.
- Inducers: (e.g., carbamazepine) will decrease aripiprazole drug concentrations; double dose when used concomitantly.
- Pregnancy: Pregnancy Category C
- Labor and Delivery: The effect is unknown.
- Nursing Mothers: Aripiprazole is excreted in human breast milk. A decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment needed.
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustment needed.
- Pediatric Patients: Safety and effectiveness in patients with major depressive disorder or agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar mania have not been established. Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients with schizophrenia, bipolar mania, those demonstrating irritability associated with autistic disorder have been established.
- Geriatric Patients: No dosage adjustment is recommended for elderly patients. The safety and efficacy of aripiprazole in the treatment of patients with psychosis associated with Alzheimer's disease has not been established. If the prescriber elects to treat such patients, vigilance should be exercised.
- Aripiprazole is excreted in human breast milk. A decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
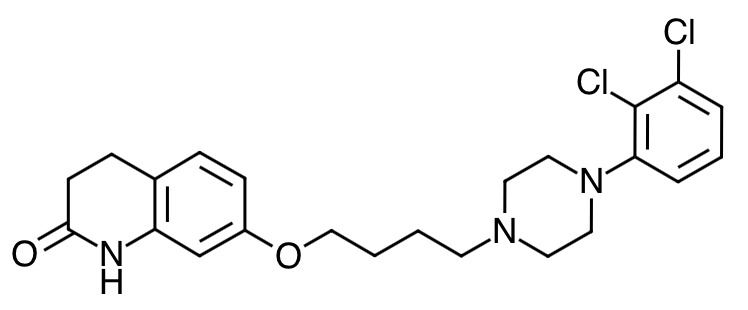
- Scientific Name: 7-[4-[4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1- piperazinyl]butoxy]-3,4-dihydrocarbostyril
- Empirical Formula: C23H27Cl2N3O2
- Molecular Weight: 448.38
- The proposed efficacy of aripiprazole is mediated through a combination of partial agonist activity at D2 and 5-HT1A receptors and antagonist activity at 5-HT2A receptors. Actions at receptors other than D2, 5-HT1A, and 5-HT2A may explain some of the other clinical effects of aripiprazole (e.g., the orthostatic hypotension observed with aripiprazole may be explained by its antagonist activity at adrenergic alpha1 receptors).
- Aripiprazole exhibits high affinity for dopamine D2 and D3, serotonin 5-HT1A, and 5-HT2A receptors (Ki values of 0.34 nM, 0,8 nM, 1.7 nM, and 3.4 nM, respectively), moderate affinity for dopamine D4, serotonin 5-HT2C and 5-HT7, alpha1-adrenergic and histamine H1 receptors (Ki values of 44 nM, 15nM, 39 nM, 57 nM and 61 nM, respectively), and moderate affinity for the serotonin reuptake site (Ki=98 nM). Aripiprazole has no appreciable affinity for cholinergic muscarinic receptors (IC50>1000 nM).
- Aripiprazole functions as a partial agonist at the dopamine D2 and the serotonin 5-HT1A receptors, and as an antagonist at serotonin 5-HT2A receptor.
- Activity is presumably primarily due to the parent drug, aripiprazole, and to a lesser extent, to its major metabolite, dehydro-aripiprazole, which has been shown to have affinities for D2 receptors similar to the parent drug and represents 40% of the parent drug exposure in plasma. The mean elimination half-lives are about 75 hours and 94 hours for aripiprazole and dehydro-aripiprazole, respectively. Steady-state concentrations are attained within 14 days of dosing for both active moieties. Aripiprazole accumulation is predictable from single-dose pharmacokinetics. At steady- state, the pharmacokinetics of aripiprazole are dose-proportional. Elimination of aripiprazole is mainly through hepatic metabolism involving two P450 isozymes, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4.
- Pharmacokinetic studies showed that the orally disintegrating tablets are bioequivalent to tablets.
- Bioavailability:
- Peak plasma concentrations occurring within 3 hours to 5 hours; the absolute oral bioavailability of the tablet formulation is 87%.
- ABILIFY can be administered with or without food.
- Volume of Distribution: is high (404 L or 4.9 L/kg), indicating extensive extravascular distribution. Protein Binding: Greater than 99% bound to serum proteins, primarily to albumin.
- Metabolism: Aripiprazole is metabolized primarily by three biotransformation pathways: dehydrogenation, hydroxylation, and N-dealkylation. Based on in vitro studies, CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 enzymes are responsible for dehydrogenation and hydroxylation of aripiprazole, and N-dealkylation is catalyzed by CYP3A4. Aripiprazole is the predominant drug moiety in the systemic circulation. At steady-state, dehydro- aripiprazole, the active metabolite, represents about 40% of aripiprazole AUC in plasma.
- Approximately 8% of Caucasians and 3-8% of Black/African Americans lack the capacity to metabolize CYP2D6 substrates and are classified as poor metabolizers (PM), whereas the rest are extensive metabolizers (EM). PMs have about an 80% increase in aripiprazole exposure and about a 30% decrease in exposure to the active metabolite compared to EMs, resulting in about a 60% higher exposure to the total active moieties from a given dose of aripiprazole compared to EMs. Coadministration of aripiprazole with known inhibitors of CYP2D6, such as quinidine or fluoxetine in EMs, approximately doubles aripiprazole plasma exposure, and dose adjustment is needed. Similarly, PMs have higher exposure to aripiprazole compared to EMs; hence, PMs should have their initial dose reduced by one-half. Laboratory tests are available to identify CYP2D6 PMs. The mean elimination half-lives are about 75 hours and 146 hours for aripiprazole in EMs and PMs, respectively. Aripiprazole does not inhibit or induce the CYP2D6 pathway.
- Elimination: Following a single oral dose of [14C]-labeled aripiprazole, approximately 25% and 55% of the administered radioactivity was recovered in the urine ad feces, respectively. Less than 1% of unchanged aripiprazole was excreted in the urine and approximately 18% of the oral dose was recovered unchanged in the feces.
- Intramuscular Administration: The median times to the peak plasma concentrations were at 1 hour and 3 hours. A 5 mg intramuscular injection of aripiprazole had an absolute bioavailability of 100%.
- Patients and caregivers should be advised that elderly patients with dementia-related psychoses treated with antipsychotic drugs are at increased risk of death. Aripiprazole is not approved for elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis.
- Patients, their families, and their caregivers should be encouraged to be alert to the emergence of anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, aggressiveness, impulsivity, akathisia (psychomotor restlessness), hypomania, mania, other unusual changes in behavior, worsening of depression, and suicidal ideation, especially early during antidepressant treatment and when the dose is adjusted up or down. Families and caregivers of patients should be advised to look for the emergence of such symptoms on a day-to-day basis, since changes may be abrupt. Such symptoms should be reported to the patient's prescriber or health professional, especially if they are severe, abrupt in onset, or were not part of the patient's presenting symptoms. Symptoms such as these may be associated with an increased risk for suicidal thinking and behavior and indicate a need for very close monitoring and possibly changes in the medication. Prescribers or other health professionals should inform patients, their families, and their caregivers about the benefits and risks associated with treatment with ABILIFY and should counsel them in its appropriate use. A patient Medication Guide including information about "Antidepressant Medicines, Depression and other Serious Mental Illness, and Suicidal Thoughts or Actions" is available for ABILIFY. The prescriber or health professional should instruct patients, their families, and their caregivers to read the Medication Guide and should assist them in understanding its contents. Patients should be given the opportunity to discuss the contents of the Medication Guide and to obtain answers to any questions they may have. It should be noted that ABILIFY is not approved as a single agent for treatment of depression and has not been evaluated in pediatric major depressive disorder.
- Advise patients that are taking the orally disintegrating tablet to not open the blister until ready to administer. Do not push the tablet through the foil (peel back the foil) because this could damage the tablet. Immediately upon opening the blister, using dry hands, remove the tablet and place the entire tablet on the tongue. Tablet disintegration occurs rapidly in saliva. It is recommended that the tablet be taken without liquid. However, if needed, it can be taken with liquid. Do not attempt to split the tablet.
- Patients should be cautioned about operating hazardous machinery, including automobiles, until they are reasonably certain that therapy does not affect them adversely.
- Patients should be advised to notify their physician if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during therapy.
- Patients should be advised not to breast-feed an infant if they are taking aripiprazole.
- Patients should be advised to inform their physicians if they are taking, or plan to take, any prescription or over-the-counter drugs, since there is a potential for interactions.
- Patients should be advised to avoid alcohol while taking aripiprazole.
- Patients should be advised regarding appropriate care in avoiding overheating and dehydration.
- Patients should be advised that each mL of aripiprazole oral solution contains 400 mg of sucrose and 200 mg of fructose.
Indications
Dosing
Dosage Forms
Black Box Warnings
Warnings
Overdose
Drug Interactions
Special Populations
Breastfeeding
Chemical Structure
Mechanism of Action
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacokinetics
Counseling Points
MESH Terms & Keywords
|
|---|
|